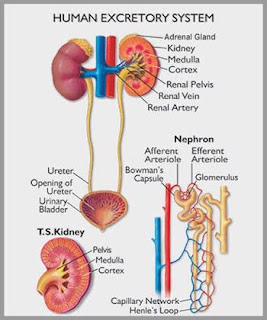
Answers of Quiz 1750 (Pilgrimage/Hajj)
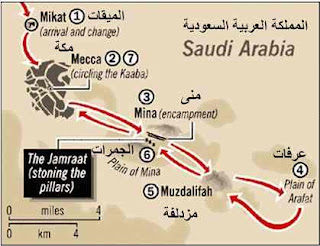
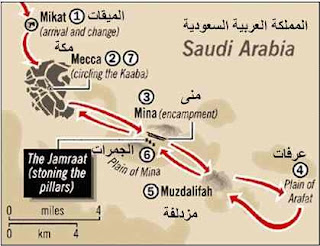
1. To intend a journey 2. On 8 Dhu al-Qa'dah 8 AH 3. 5th 4. Sahab-e-Istita'at 5. In 9 AH 6. In 10 AH 7. 1 time 8. Hazrat Abu Bakr (RA) 9. A person who performs Hajj. 10. Ihram is a special spiritual state in which pilgrim wear two whije sheets of seamless cloth & abstain from certain things. 11. Walking counter-clockwise 7 times around the Ka'aba 12. Stonning to Satan 13. Sayee 14. A place designated for changing into Ihram 15. Ihram at Mina, Mina to Arafat 16. Standing before Allah, prayers in Namirah Masjid, Arafat to Muzdalifa 17. Ramy al-Jamarat, Back to Mina, animal slaughter, Shaving head 18. Stonning of the Devil 19. Stonning, return to Mecca 20. Return to Mecca after stonning (if not returned on 12 Zil Hajj) 21. Muzdalifa is a place between Mina & Arafat 22. Umrah 23. Yaum-e-Arfa 24. Yaum-e-Nahar 25. Hajj-e-Akbar 26. Hajj Day on Juma 27. Umrah 28. The state of being physically & financially capable of performing the Hajj 2...